In considering the many ills that face society, there has been a large focus on the socio-economic status of the family or of the individual in the desire to explain the condition at hand. For example, if a child grows up to become a criminal, we ask, “what was the socio-economic condition of that child or his parents?”
The idea behind this, of course, is that if we can isolate the failure to the economic inequality of society, then we can begin to “fix it” through governmental programs bent on promoting “equality.”
But what if there was another reason why people did the things they do? In this section, I speak about Parenting as discussed in the book, “The Bell Curve.”
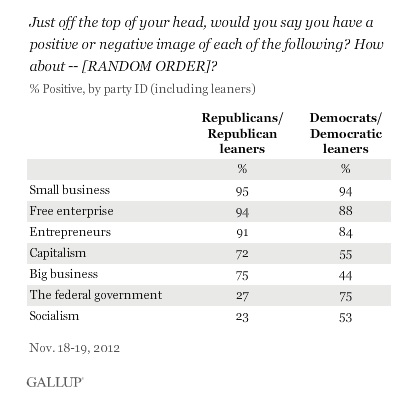
In the chapter regarding parenting, the first condition discussed is low birth weight babies. Previously I have shown data that suggests that the SES status of the mother has little bearing on the determination of that condition in children.
But IQ:
As mentioned, the impact of the socio-economic status of the mother is nominal; the IQ of the mother is not. A low IQ has a major impact on the chance of a baby being born with a low birth weight; SES – not as much.
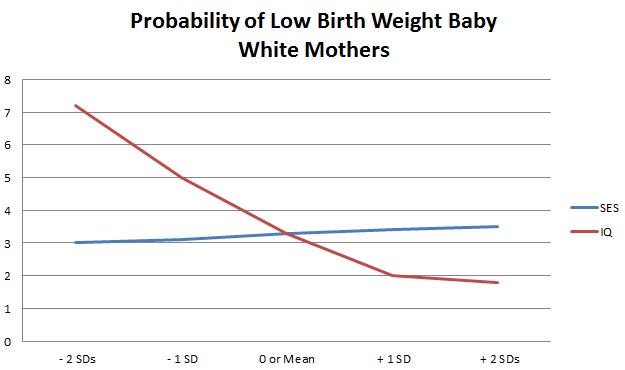
After being born, the child must face life. Specifically the prospect of being poor. Initially, the authors held all variable constant and displayed the prospects of a child remaining poor in the fist 3 years of life based on the mother’s SES. It didn’t look good. But what happens if we include IQ:
No change. The poverty rate of the child is equally determined by the SES and the IQ of the mother. With the data showing such an exact match as both SES and IQ moved from low to high, I suspect that there is a case where one is determined by the other.
Again, following the sections in this chapter, the topic switches to the Home Index:
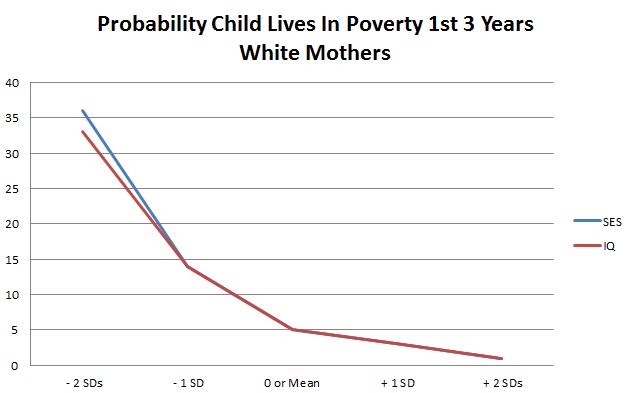
The Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment (HOME) Inventory is designed to measure the quality and extent of stimulation available to a child in the home environment. The Infant/Toddler HOME Inventory (IT-HOME) comprises 45 items that provide information from the child’s perspective on stimuli found to affect children’s cognitive development. Assessors make observations during home visits when the child is awake and engaged in activities typical for that time of the day and conduct an interview with a parent or guardian. The IT-HOME is organized into six subscales: (1) Responsivity: the extent of responsiveness of the parent to the child; (2) Acceptance: parental acceptance of suboptimal behavior and avoidance of restriction and punishment; (3) Organization: including regularity and predictability of the environment; (4) Learning Materials: provision of appropriate play and learning materials; (5) Involvement: extent of parental involvement; and (6) Variety in daily stimulation. For the IT-HOME, 18 items are based on observation, 15 on interview, and 12 on either observation or interview.
This index was applied to the population in the study and the result showed that the socio-economic status of the mother played a role in the HOME Index rating. However, IQ played an even more significant role:
 As you can see, a lower IQ is more devastating than a poor mother while I high IQ is more beneficial than a wealthy mother.
As you can see, a lower IQ is more devastating than a poor mother while I high IQ is more beneficial than a wealthy mother.
As the child grows, the development of the child can be impacted by the conditions of the home, poverty and parenting skills are, of course, two of those conditions. In an attempt to measure this development, the authors conducted a survey of 4 developmental indicators and if a child scored in the bottom decile for any of the 4, they scored a “Yes” on the “development index.” If not, they scored a no.
The results:
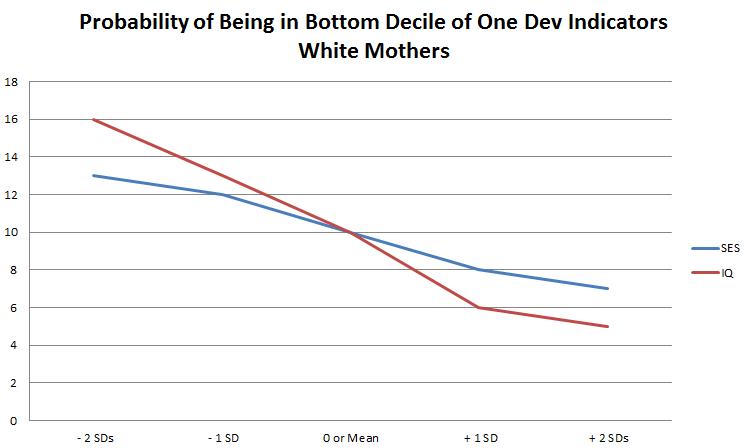 The pattern is again, presented. IQ at the low end is more detrimental than poverty while at the high end, IQ is more advantageous than being wealthy. However, in this specific study that difference is marginal.
The pattern is again, presented. IQ at the low end is more detrimental than poverty while at the high end, IQ is more advantageous than being wealthy. However, in this specific study that difference is marginal.
The final section of the chapter looks into the IQ of the child and tries to determine the significance of been raised in a home more exposed to the challenges of poverty vs. being raised in a more affluent home. Additionally, the same investigation is conducted using the key variable of IQ:
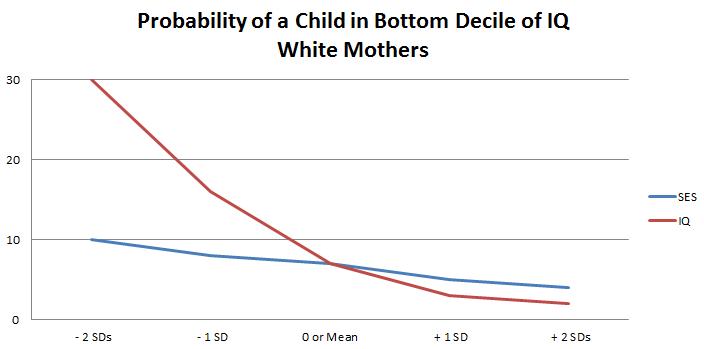 The result is consistent with data already being demonstrated in this and other chapters. The argument can be made that when isolating the socio-economic status of families and of mothers in the study the well being of the child generally suffers as that mother becomes poorer. However, when all variables are held constant save IQ, those other factors are diminished to the point of being statistically insignificant.
The result is consistent with data already being demonstrated in this and other chapters. The argument can be made that when isolating the socio-economic status of families and of mothers in the study the well being of the child generally suffers as that mother becomes poorer. However, when all variables are held constant save IQ, those other factors are diminished to the point of being statistically insignificant.
IQ matters.